Project Description
Description: I attended Interdisciplinary Contest in Modeling (ICM) in 2016 with Jianmin Deng and Jiahao Yu. We chose this topic on information network and here is our abstract.
Abstract:
In this article, we build 2 models respectively to simulate the information network and evaluate the influence of media on public opinion.
We start with defining what qualifies as news. By using a dataset of more than 39,000 entries of different levels of news, we set up a Heat Standard to evaluate value of news, and implement 5 different learning algorithms (Logistic Regression, SVN, Random Forest, K- Nearest Neighbor, C4.5 algorithm) to do the learning prediction. Random Forest algorithm has the best performance and is hence used as our news filter.
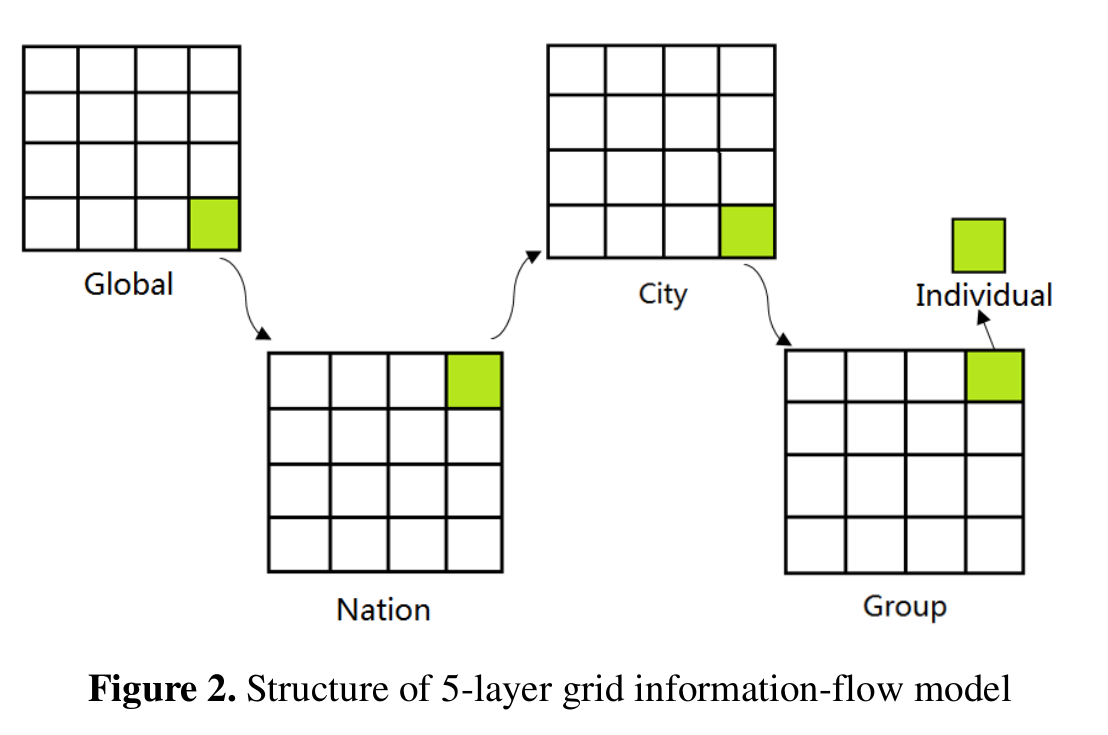
Next, we build up a 5-layer Grid Information-flow Model to simulate the real-world information network. Cellular Automata and Computational Simulation are used to analyze the speed and broadness of information transmission in different historical stages. Every grid unit in different layer can represent individual, group, city or nation. And every piece of news is an information unit that have defined dynamics to interact with every gird. This strategy lays a solid foundation in simulating geographic limit and difference in transmission capacity. Stratification also allow us to maintain the essential topology feature within individual network as well as network between individual and media. Our result shows accuracy and stability in fitting current information communication situation. A prediction is made about the situation in 2050.
Finally, we discuss three famous theories of media influence on public and build our second model to investigate the media effects on public opinion. BA Scale-free Network and Epidemic SIER Model are used to represent current information flow through Internet. We find that the intensity of media coverage and the number of media involved in the transmission are two key factors on the number of people accepting the idea proposed by public media. Greater coverage intensity and larger number of media lead to deeper influence on public opinions.
47471-2